The BUPTCampus dataset is constructed for video-based visible-infrared person re-identification. We adopt six binocular bimodal cameras to capture RGB and IR modalities simultaneously with approximate pixel-alignment. To ensure the diversity of samples, different cameras and engines are used to capture videos with various color styles, resolutions, frame rates and binocular synchronization modes. For labeling, all RGB videos are processed by the multi-object tracking algorithm SiamMOT to predict tracklets, which are further revised manually. Then cross-camera IDs are annotated manually. Benefiting from the synchronization mode of bimodal cameras, the bounding boxes and IDs of IR samples are automatically generated with RGB labels. Figure 1 visualize several samples from BUPTCampus.
Figure 1. Samples visualization from BUPTCampus.
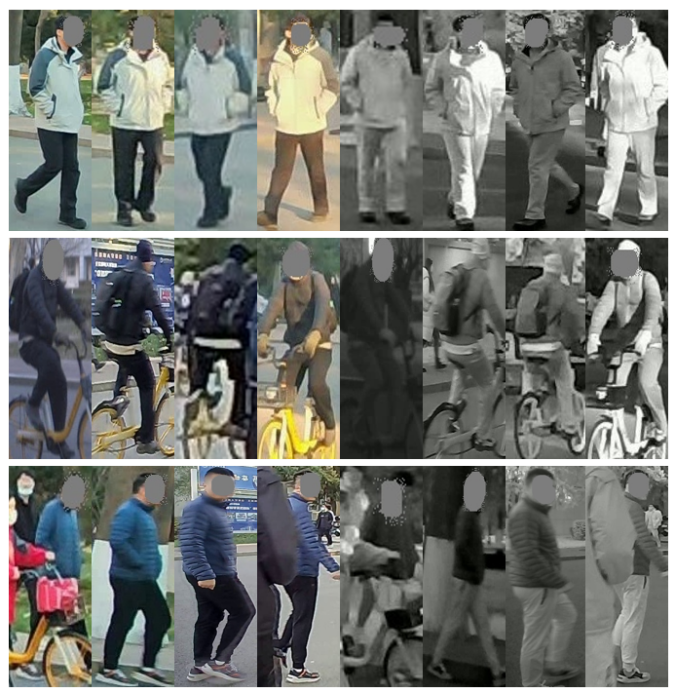

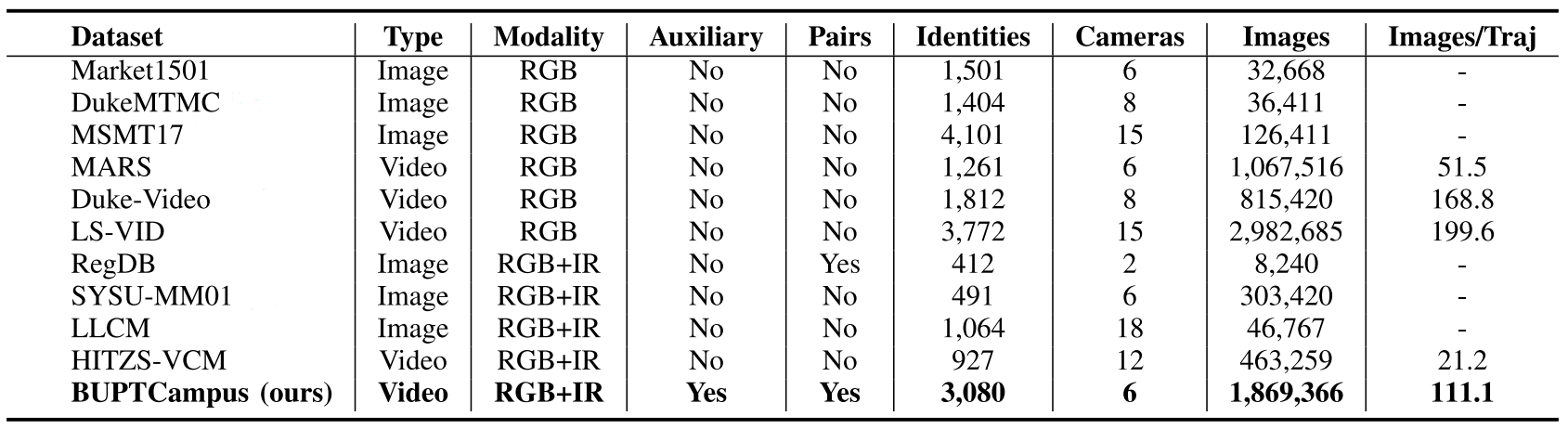
The comparison between BUPTCampus and several common ReID datasets are shown in Table 1. Specifically, BUPTCampus distinguishes itself from previous datasets in the following aspects:
1) Instead of images, it collects tracklets as samples, enabling to exploit the temporal cues.
2) It contains pixel-aligned RGB/IR sample pairs captured by binocular cameras, which can facilitate modality-invariant learning.
3) It is much larger than existing VI-ReID datasets with 3,080 identities, 16,826 tracklets and 1,869,366 images. Different styles of cameras are used to ensure the diversity of samples.
4) Existing ReID tasks focus on the cross-camera matching problem, and those identities who appear only once are commonly ignored in training. However, these samples are easy to obtain in reality, and would help the learning. We take vast single-camera samples into consideration, and call them auxiliary samples, and accordingly, the main training samples, i.e., multiple-camera samples, are called primary samples.
Table 1. Comparison among common person re-identification datasets.